Human Resource Management
What is human resource management (HRM)?
Human resource management (HRM) is the practice of recruiting, hiring, deploying and managing an organization's employees. HRM is often referred to simply as human resources (HR). A company or organization's HR department is usually responsible for creating, putting into effect and overseeing policies governing workers and the relationship of the organization with its employees. The term human resources was first used in the early 1900s, and then more widely in the 1960s, to describe the people who work for the organization, in aggregate.
HRM is employee management with an emphasis on employees as assets of the business. In this context, employees are sometimes referred to as human capital. As with other business assets, the goal is to make effective use of employees, reducing risk and maximizing return on investment (ROI).
The modern term human capital management (HCM) is often used by large and midsize companies when discussing HR technology.
The importance of human resource management
The purpose of HRM practices is to manage the people within a workplace to achieve the organization's mission and reinforce the corporate culture. When people management is done effectively, HR managers can help recruit new employees who have the skills to further the company's goals. HR professionals also aid in the training and professional development of employees to meet the organization's objectives.
A company is only as good as its employees, making HRM a crucial part of maintaining or improving the health of the business. Additionally, HR managers monitor the state of the job market to help the organization stay competitive. This could include ensuring compensation and benefits are competitive, events are planned to keep employees from burning out and job roles are adapted based on the market.
How does HRM work?
HR professionals manage the day-to-day execution of HR-related functions. Typically, human resources is a standalone department within an organization.
HR departments vary in the size, structure and nature of their individual positions. For small organizations, one HR generalist might perform a broad array of functions. Larger organizations have several HR professionals who handle specialized roles, such as recruiting, immigration and visas, talent management, employee benefits and compensation. Though these HR positions are specialized, job functions might still overlap.
Amazon is an example of a large company with multiple types of specialized HR positions. The company's career website lists the following HR job titles:
- HR assistant.
- HR business partner.
- HR manager.
- Recruiter.
- Recruiting coordinator.
- Recruiting manager.
- Immigration specialist.
- Leave of absence and accommodation specialist.
- Compensation specialist or manager.
- Benefits specialist or manager.
- Talent management specialist or manager.
- Learning and development specialist or manager.
- HR technology or process project program manager.
- HR analytics specialist or manager.
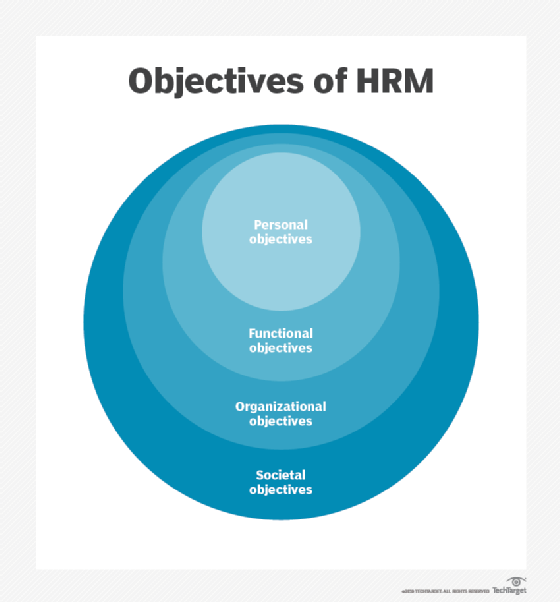
Objectives of human resource management
HRM can be broken down into the following four category objectives:
- Societal objectives. These are measures put in place to respond to the ethical and social needs or challenges of the company and its employees. This includes legal issues such as equal opportunity and equal pay for equal work.
- Organizational objectives. These are actions taken to ensure organizational efficiency, including providing the appropriate training, hiring the right number of employees for a given task and maintaining high employee retention rates.
- Functional objectives. These are the guidelines used to keep HR functioning properly within the organization. They include ensuring all HR resources are allocated to their full potential.
- Personal objectives. These are the resources used to support the personal goals of each employee. They include opportunities for education and career development, as well as maintaining employee satisfaction.
More specific objectives of HRM include the following:
- Provide and maintain productive employees.
- Make full use of the skills and abilities of each employee.
- Ensure employees have and receive the proper training.
- Build and maintain a positive employee experience with high satisfaction and quality of life, so that employees can contribute their best efforts to their work.
- Communicate company policies, procedures, rules and regulations to employees.
- Maintain ethical, legal and socially responsible policies and behaviors in the workplace.
- Manage internal and external changes that might affect employees and staffing.
Skills and responsibilities of an HR manager
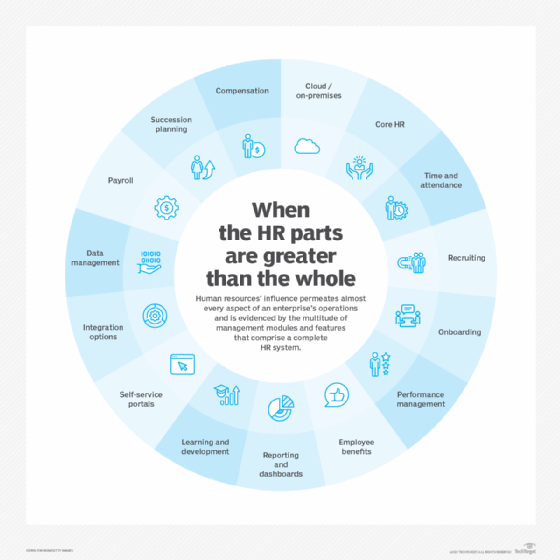
HRM is typically broken into pre-employment and employment phases, as well as more specific subsections, with an HR manager assigned to each one. Areas of HRM oversight include the following:
- Employee recruitment.
- Onboarding and retention.
- Talent and workforce management.
- Job role assignment.
- Career development.
- Compensation and benefits.
- Labor law compliance.
- Performance management.
- Training and development.
- Succession planning.
- Employee engagement and recognition.
- Team building.
HR managers benefit from having skills and experience in a range of areas. The most essential HRM skills that professionals should possess include the following:
- Communication. A high-level of verbal and written capabilities is required in most HRM jobs.
- Recruitment and talent acquisition. Tasks in this area include writing job descriptions, conducting interviews, assessing candidates, negotiating offers and onboarding new employees.
- Employee relations. HR managers must have labor relations skills to address grievances and build positive employee experiences.
- Compliance with legal requirements. HR managers must be up to date with employment laws and regulations.
- Conflict management and resolution. Mediation capabilities help HR managers resolve conflicts and other difficult situations.
- Performance management. Managers must set performance standards and help employees develop skills to achieve them.
- Strategic thinking. HR manager jobs require high-level thinking, such as aligning HR strategies with the company's goals.
- Analytics. Data analysis skills help analyze workforce metrics and provide insights for decision-making.
- Adaptability. HR managers must be able to deal with changing workplace and societal issues on an ongoing basis.
- Ethics and confidentiality. These skills require knowledge of confidentiality and privacy requirements, as well as general and industry-specific ethical standards.
HRM software
Almost all areas of HRM have sophisticated software that automates HR processes to varying degrees, along with other features, such as analytics. For example, job candidate recruiting has seen enormous growth in the number of software tools and management systems that match employers and job candidates. Those systems also manage other steps in the hiring process, such as interviewing and vetting.
HRM software is often provided as on-premises systems. However, nearly every area of HR tech has moved to cloud-based software-as-a-service platforms.
There are several vendors in the HRM market, including ADP, BambooHR, HROne, Isolved, Paycom, Paylocity, Personio, Rippling, SAP and Workday.
Good information
ReplyDelete